Both dental implants and veneers are common options within cosmetic dentistry. While they aim to improve the appearance and functionality of your teeth, they serve distinct purposes and involve different procedures. Understanding the differences between these options can help individuals seeking a cosmetic dentist assess which might better suit their needs or preferences.
What Are Dental Implants?
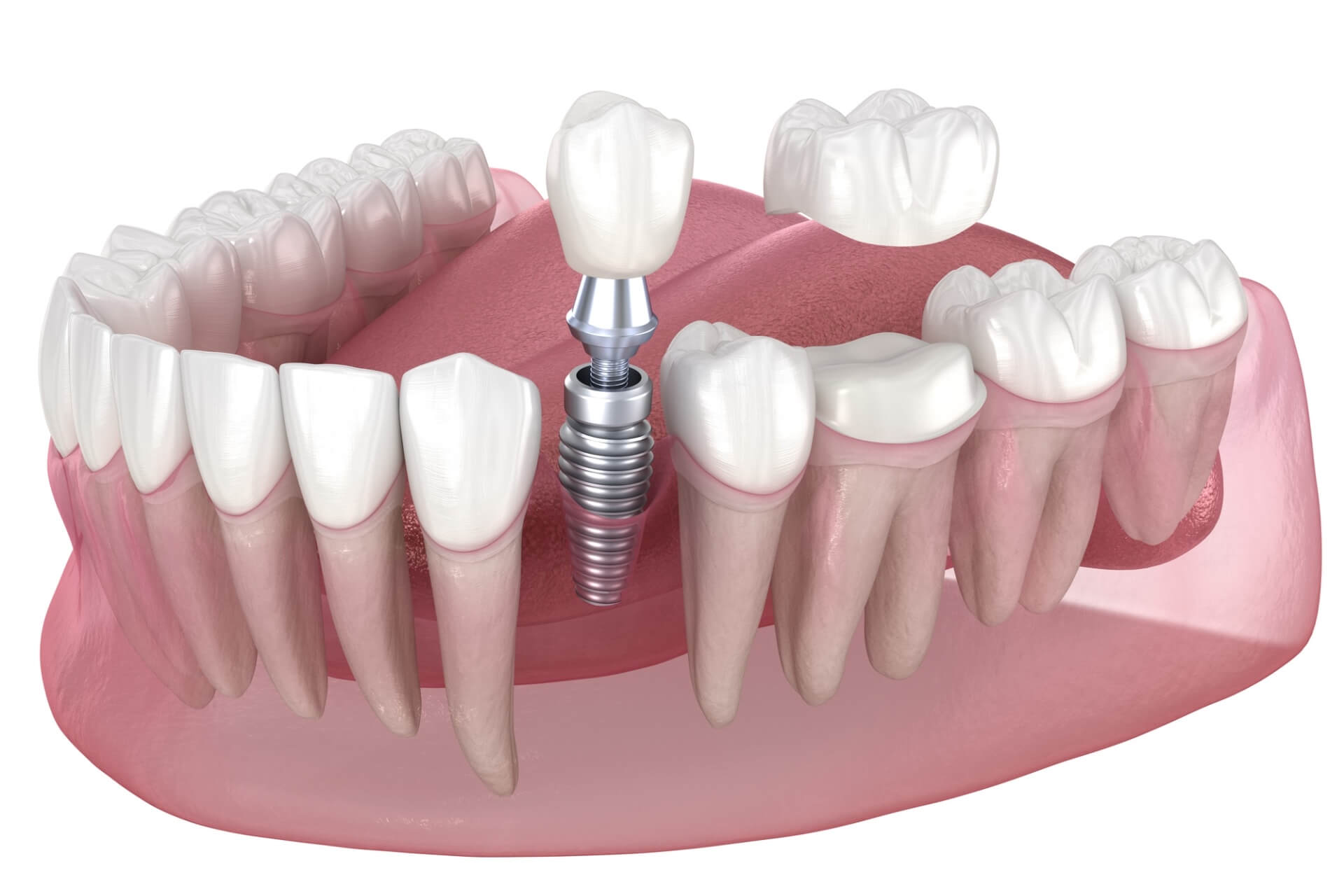
Dental implants are a long-term solution used to replace missing teeth. They consist of a titanium post surgically placed into the jawbone, acting as an artificial tooth root. The post integrates with the jawbone over time, creating a stable foundation for an artificial tooth, also known as a crown.
Dental implants are designed for individuals who are missing one or more teeth and wish to restore both the function and appearance of their teeth. Implants are customized to match the color and shape of surrounding teeth, providing a natural-looking result. The process involves several steps, beginning with an evaluation by your dentist, followed by surgical placement of the implant. After a healing period, the crown or artificial tooth is added.
What Are Veneers?
Veneers are thin, custom-made shells that cover the front surface of teeth to enhance their appearance. Often made from porcelain or resin composite materials, they are directly bonded to the tooth surface. Veneers are not designed to replace missing teeth, but rather to improve the aesthetic of existing teeth.
Individuals with uneven, stained, chipped, or slightly misaligned teeth often seek veneers to enhance their smile. Veneers can provide a consistent and polished appearance, making them ideal for cosmetic enhancements. The process typically includes an initial consultation with a cosmetic dentist, during which impressions of the teeth are taken. A small amount of enamel is then removed from the tooth’s surface to make certain the veneer fits seamlessly.
How Do Veneers and Dental Implants Differ?
Materials and Longevity
Dental implants are typically made from titanium, a durable and biocompatible material. They are designed to integrate with the bone, offering high durability and stability. The crown attached to the implant is usually crafted from ceramic or other long-lasting dental materials.
Veneers are less invasive and are made of porcelain or resin composites. Porcelain veneers are known to resist staining and mimic the properties of natural teeth, while resin veneers offer a thinner alternative. Both types are designed for durability, though they may not last as long as implants.
Functionality
Dental implants serve both functional and aesthetic purposes. They allow individuals to chew food effectively and can restore clear speech in cases where tooth loss affected pronunciation. They also help maintain the structural integrity of the jawbone, which can otherwise weaken due to missing teeth.
Veneers focus on aesthetics. They do not alter the function of the teeth but instead enhance the appearance of an individual’s smile. Veneers are not a replacement option for missing teeth and are suited for cosmetic purposes.
Maintenance and Care
Both dental implants and veneers require regular care to maintain their condition. Dental implants function similarly to natural teeth and should be brushed and flossed daily. Routine dental check-ups are also recommended to monitor the surrounding tissue and gums.
Veneers require extra caution to avoid chipping or cracking. Using a soft-bristle toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste is recommended. Individuals with veneers may be advised to avoid certain foods that could damage the veneer surface.
Consult With a Cosmetic Dentist Today
Choosing between dental implants and veneers largely depends on individual goals and oral health needs. While implants are intended to replace missing teeth and restore functionality, veneers focus on enhancing the appearance of existing teeth. Consulting with a cosmetic dentist can provide a detailed understanding of which option aligns better with specific preferences and dental conditions.